
OT Cybersecurity: What It Is and Why It Matters
We live in a hyperconnected world. Think about the power that lights your house, the water you drink or the factories making everyday products. All possible due to OT systems running behind the scenes.
But here’s the catch, industries are adopting OT and combining it with IT to increase efficiency, they have also become vulnerable to cybersecurity threats.
And the problem with it is that these systems are very old and were not designed with cybersecurity in mind. Facilities are now becoming the target of hackers, and the impact is much more serious than data breaches. We are discussing operational downtime, equipment damage, environmental risks, and even risks to human life.
This article discusses the nature of OT cybersecurity, its importance today more than ever, the peculiarities of OT systems, and which challenges organizations encounter when striving to keep them safe.
Components of OT Cybersecurity
OT cybersecurity is about protecting the systems that keep our industries running. Unlike IT systems, which focus solely on security of data, it also keeps the operations continuous, safe, and reliable. Any cyberattack on industries like energy, manufacturing, transportation, and utilities, etc., can result in massive operation disruption, damage to equipment, environmental risks, and even endangering human lives.
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
ICS systems connect sensors, software and controllers to keep the operations running. This system is commonly connected to the IT system. This makes them an easy target for cyber-attacks like Malware, ransomware, and hackers gaining remote access.
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems
SCADA systems collect data from equipment spread across a large area and display it on their dashboards. They use it to monitor and control operations in real time.
When SCADA is attacked, the impact can be big. Take the LockerGoga ransomware as an example. This ransomware attack attacked companies like Norsk Hydro or Altran and caused their operations to shut down. It forced computers to shut down which caused production shutdowns, and they had to go back to manual functioning during this crisis.
This attack was a wake-up call. OT security breaches are not just about stolen data; they can disrupt entire supply chains and put human lives at risk.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs are used to control machines, assembly lines, and automate processes. By collecting data from sensor data and sending instructions to machinery.
But the older PLCs were built when networks were air-gapped, and cybersecurity was not a major concern. Newer PLCs offer more connectivity but are also more exposed. If attackers gain access, they can manipulate these systems and cause damage.
- Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
DCS are designed to manage complex processes within a single facility. Integrating IT with OT has made them smarter but at the same time more exposed to threats.
The Triton malware attack is a chilling example. It attacked the safety instrument systems of a petrochemical plant and could have crippled emergency shutdown systems, which could have caused chemical leaks or explosions.
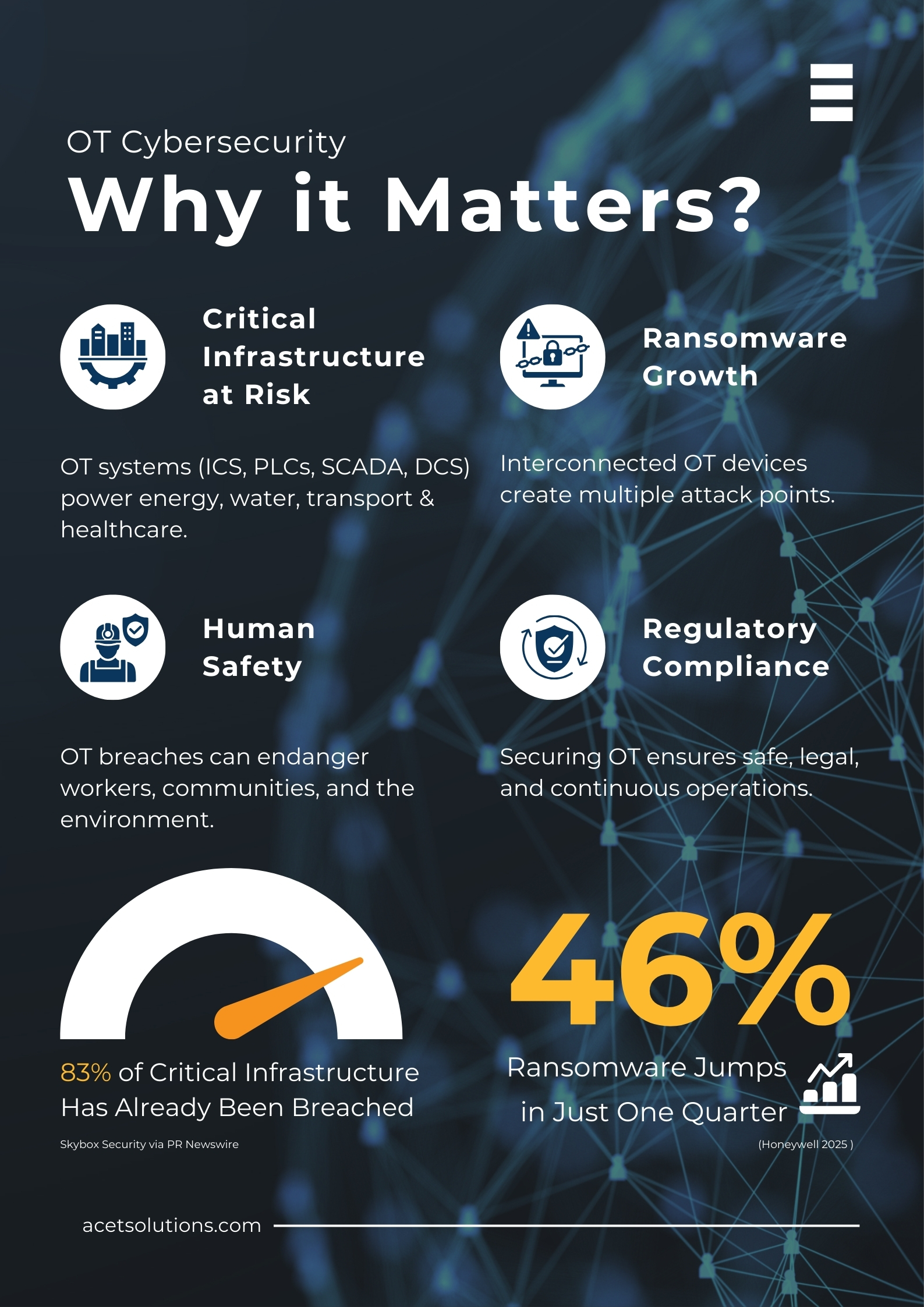
4 Reasons Why OT Cybersecurity is Important Than Ever
- Legacy Infrastructure at Risk: Many OT systems still run on legacy systems which were not built for today’s cyberworld. A survey by Skybox Security identified that 83 percent of organizations had fallen victim to an OT cyber-attack in the last 36 months, including organizations such as energy and water, services.
- In 2017, the Triton (Trisis) malware attacked a petrochemical plant’s safety system because it was unpatched. It almost caused a chemical leak by nearly disabling an emergency shutdown.
- In 2018, WannaCry ransomware spread to the OT network of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC). Unpatched windows 7 let it infect the operations and equipment stopping the production.
Not updating or segmenting the networks is a major cause for these attacks.
- Ransomware Growth: According to Honeywell 2025 Cyber Threat Report, the percentage of ransomware attacks on industrial operators increased by 46 percent between late 2024 and early 2025. In the same quarter, 2,472 potential ransomware attacks were recorded, and this is about 40 percent of all the cases recorded in 2024.
- Human Safety Concerns: Think of a chemical plant where the pipeline pumps are filled with hazardous materials at high pressure. When attackers interfere with the control systems, they might activate leaks, fires, or explosions and endanger the lives of the workers in the plant and surrounding communities. It is one of the most dreadful aspects of OT cyberattacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliances like NIST and IEC 62443 can help an organization to build a road map to help themselves.
- Protect Critical Infrastructure: Regular vulnerability scans and patch management help to reduce risk from outdated systems.
- Prevent Ransomware: Network segmentation which helps stop ransomware being overspread.
- Mitigate Risks to Human Life: Training and drills directly help the teams to respond safely and efficiently.
Differences Between OT and IT Cybersecurity
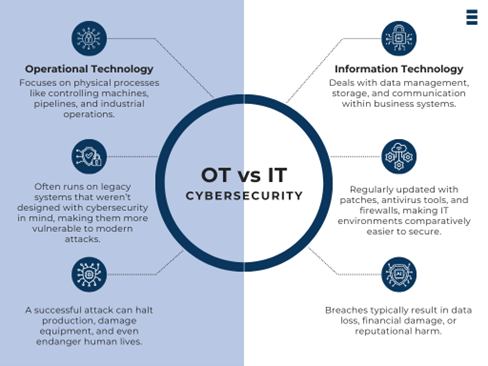
IT and OT may sound interchangeable in the context of cybersecurity, yet they cannot be more different. IT is concerned with information security that ensures information is safe, sturdy, and available. OT concerns physical systems and industrial processes that make sure that machines, plants, and critical infrastructure work well and safely.
One of the biggest mistakes that organizations make is to treat OT security just like IT security. The risks, challenges and priorities, everything is entirely different.
Three major differences include:
- Nature of Systems and Priorities
- OT systems control functions such as turbines, water flow, assembly lines, and power grids. The downtime of seconds can result in huge disruption, financial losses and safety risks. It is all about maintaining operations in a stable and safe way.
- IT systems deal with data such as customer information, financial data, emails, and business programs. Top priorities are privacy, data accuracy, and data availability.
- Security Challenges and Vulnerabilities
- Most OT environments have legacy systems that were built decades ago. They don’t support modern protections like encryption and regular patching. And updating them isn’t easy either. It would require them to shut down the operations, but OT systems cannot afford any downtime even for a second.
- IT environments are more flexible. Patches, monitoring, and upgrading systems are possible with the system without causing major interruptions.
- Impact of Cyberattacks
- Breach in IT usually results in data theft, financial penalties, or reputational damage. Frustrating and costly but manageable.
- An OT cyber-attack can halt production, damage equipment, and cause serious threats to human life.
Think of a hacker in control of the pressure systems of a chemical plant or the real-world damage that is done by controls of a power grid.
5 Challenges of Securing OT Environments
- Legacy Infrastructure: The OT devices are outmoded and hard to protect.
- Operational Constraints: 24/7 operations frequently prevent patching, or even downtime.
- Lack of Skilled Workforce: OT engineers do not possess cybersecurity skills, and IT staff do not know how an industrial process works.
- Limited Network Visibility: Most organizations are unaware of all the resources allied to their OT networks.
- Regulatory Complexity: Operational pressures of regulatory compliance systems such as IEC 62443, NIST and NERC CIP.
Conclusion
Every new connection comes with a new doorway for hackers. The cost of neglecting these serious cybersecurity concerns is more than just lost data but could mean shutdowns and human lives at risk.
OT systems directly keep our world moving. Which means OT cybersecurity requires a different mindset, one with a deep understanding of what’s at stake here. It requires foresight and strategy.
Organizations that act now and implement IT-OT security strategies will not only reduce cyber threats; but can stay competitive and trusted.
OT cybersecurity is not an option anymore. It is the frontline defense of our industries and the future we depend on.
Learn more about how to secure your industrial environment, visit the website
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OT means the systems that monitor, control, machines and processes. OT cybersecurity means keeping these systems safe from attacks that can cause downtimes or shutdown productions.
OT cybersecurity is important because attacks on industrial networks can cause damage to industrial equipment, processes and even human lives.
Ransomware attacks, old and unpatched systems, and unsecured remote access.
Know your assets, network segmentation, secure remote access, monitor in real time, comply by training the team
IT protects data while OT cybersecurity protects systems and industrial processes. Breach of IT can cause loss of data and breach of OT can cause serious accidents and stop processes.
Related Articles






